Understanding the Impact of Air Quality on Respiratory Health
In the canvas of environmental factors affecting our health, the quality of the air we breathe stands out as a crucial element. Each breath we take can either nourish our bodies or expose us to harmful pollutants. With the rise in industrial activities and urbanization, the concern for air quality has never been more pertinent. This article aims to shed light on the intricate relationship between air quality and respiratory health, offering insights and practical advice to safeguard one of our most vital functions: breathing.
Understanding Air Quality and Its Components:
Air quality is determined by the concentration of pollutants in the air we breathe. Common pollutants include Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), Sulfur Dioxide (SO2), and Ozone (O3). These pollutants originate from various sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial activities, and natural events like wildfires. In urban settings, the concentration of these pollutants can be significantly higher, posing a greater risk to public health.
Exposure to poor air quality can lead to a range of respiratory problems. In the short term, it can cause irritation of the airways, coughing, and shortness of breath. Long-term exposure can lead to more severe conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and even lung cancer. The tiny particles in polluted air can penetrate deep into the lungs, causing inflammation and exacerbating existing respiratory issues.
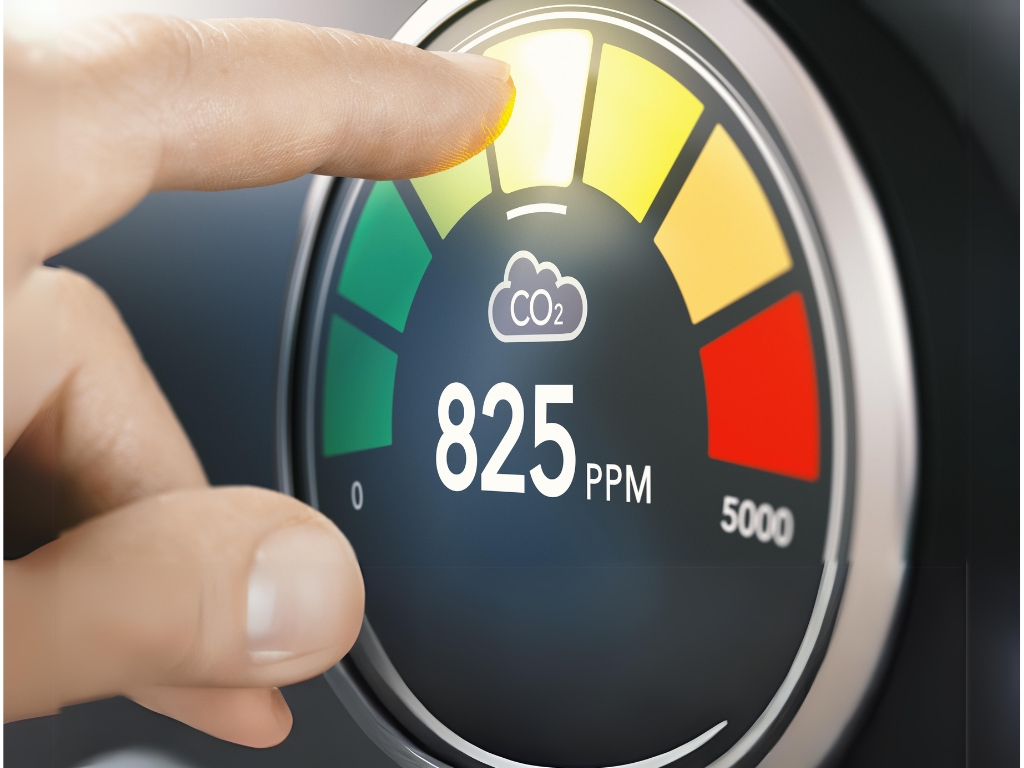
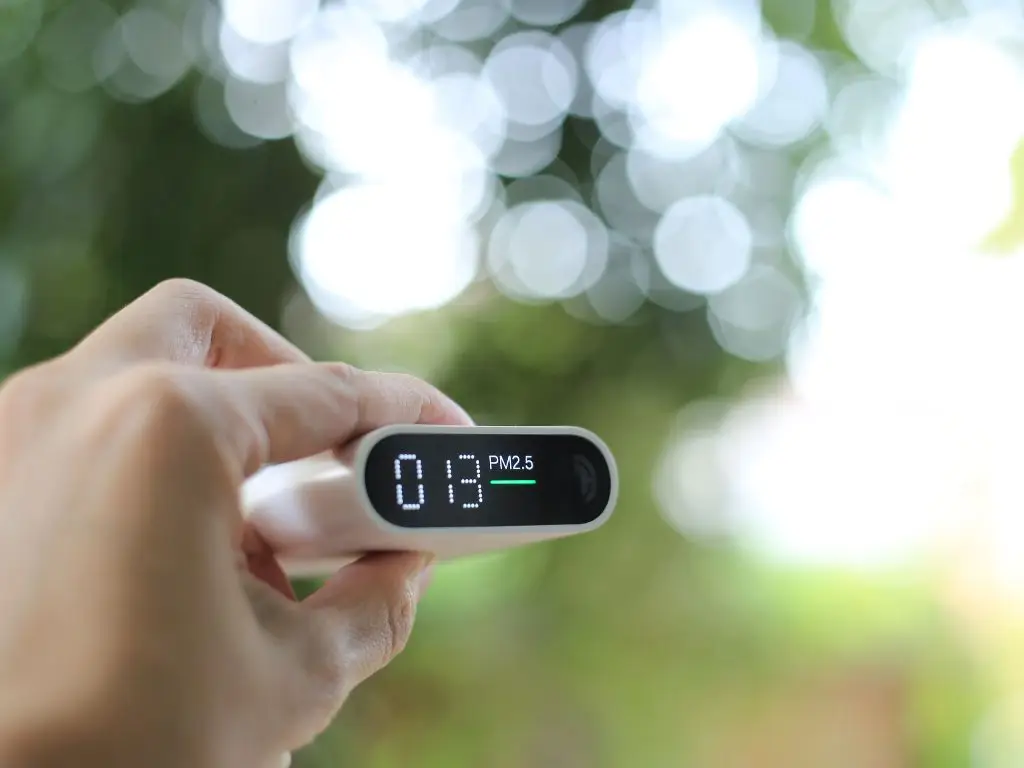
Measuring and Understanding the Air Quality Index (AQI):
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a tool used to communicate how polluted the air currently is or how polluted it is forecast to become. The AQI works on a scale from 0 to 500, where higher values indicate worse air quality and a higher potential for adverse health effects. Understanding the AQI levels is crucial for individuals, especially those in vulnerable groups, to minimize their exposure to harmful air quality.
To protect your respiratory health, consider the following tips.
Monitor the AQI in your area using reliable sources and limit outdoor activities when the air quality is poor.
Use air purifiers at home, especially if you live in a high-pollution area.
Improve indoor air quality by ensuring proper ventilation and using indoor plants that can help filter the air.
Adopt lifestyle changes that contribute to better air quality, such as using public transportation, reducing energy consumption, and advocating for cleaner energy sources.
Air quality is a significant determinant of our respiratory health. By staying informed and proactive, we can mitigate the effects of air pollution on our lungs. Awareness and action are key – whether it’s monitoring air quality, improving our indoor environment, or contributing to broader environmental efforts. Let’s prioritize our lung health by being vigilant about the air we breathe, for ourselves and for the generations to come.